README.md 15 KB
CALDER user manuel
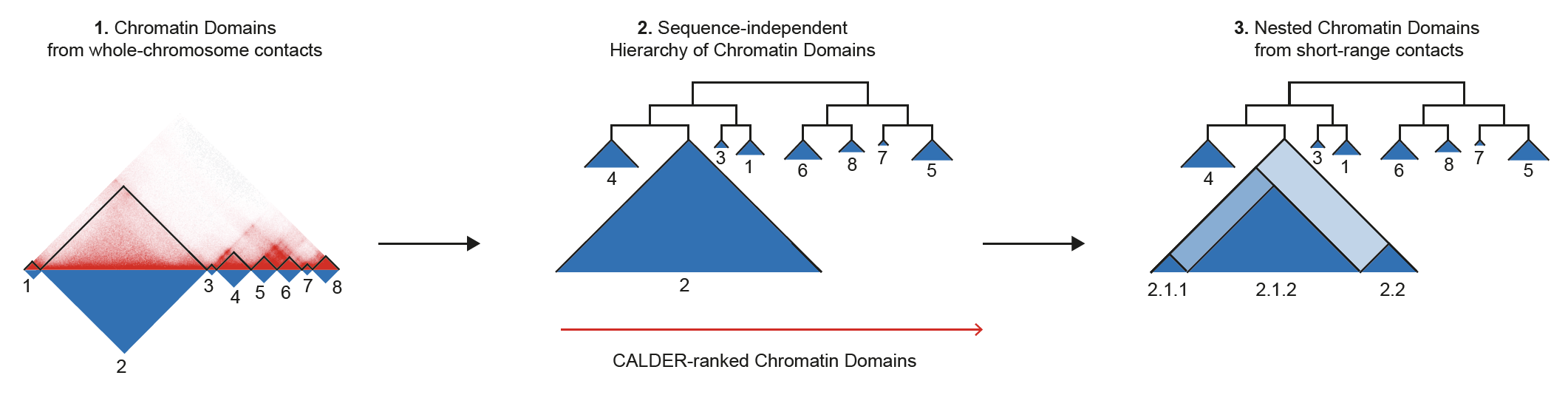
CALDER is a Hi-C analysis tool that allows: (1) compute chromatin domains from whole chromosome contacts; (2) derive their non-linear hierarchical organization and obtain sub-compartments; (3) compute nested sub-domains within each chromatin domain from short-range contacts. CALDER is currently implemented in R.
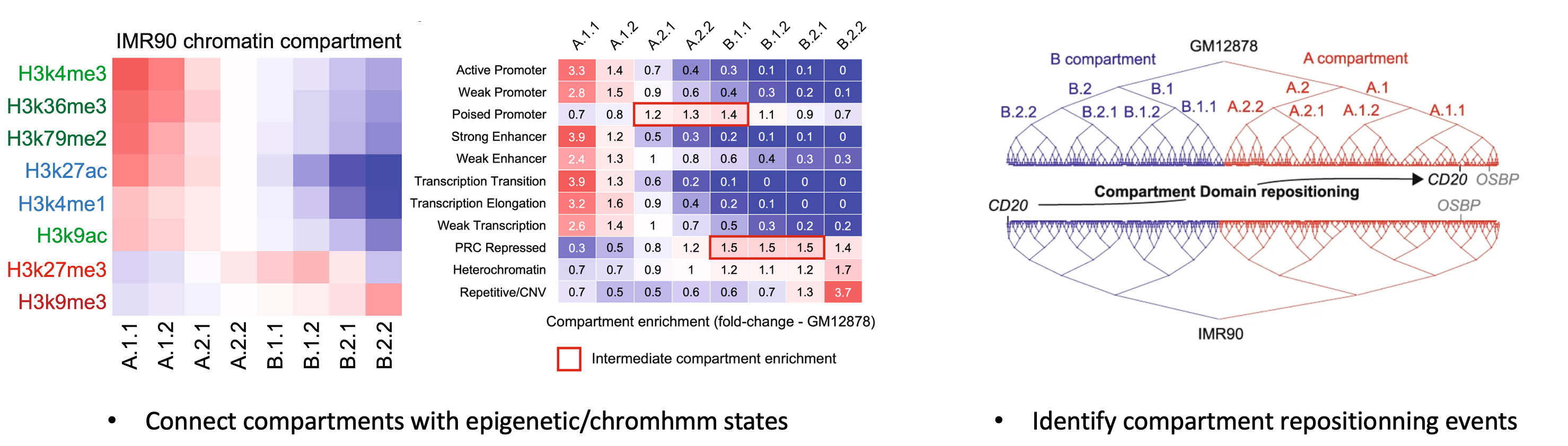
Calder connects chromatin 3D organization to genomic function:
Multiple new features were added in version 2.0
- Support for hg19, hg38, mm9, mm10 and other genomes
- Support input in .hic format generated by Juicer tools (https://github.com/aidenlab/juicer)
- Opitimized bin_size selection for more reliable compartment identification
- Aggregated all chromosome output into a single file for easier visualization in IGV
- Added output in tabular .txt format at bin level for easier downstream analysis
Below we introduce two main updates:
(1) Opitimized bin_size selection
Due to reasons such as low data quality or large scale structrual variation, compartments can be unreliablly called at one bin_size (equivalent to resoltution in the literature) but properly called at another bin_size. We added an opitimized bin_size selection strategy to call reliable compartments. This strategey is based on the observation from our large scale compartment analysis (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-22666-3), that although compartments can change between different conditions, their overall correlation cor(compartment_rank_1, compartment_rank_2) is high (> 0.4).
The strategy: given a bin_size specified by user, we call compartments with extended bin_sizes and choose the smallest bin_size such that no bigger bin_size can increase the compartment correclation with a reference compartment more than 0.05. For example, if correclation for bin_size=10000 is 0.2 while for bin_size=50000 is 0.6, we are more confident the latter is more reliable; if correclation for bin_size=10000 is 0.5 while for bin_size=50000 is 0.52, we would choose the former as it has higher resolution.
bin_size is extended in the following way thus to aggregate directly from the input contact matrix into larger bin_sizes, without the need to provide additional contact matrices from user side
if(bin_size==5E3) bin_sizes = c(5E3, 10E3, 50E3, 100E3)
if(bin_size==10E3) bin_sizes = c(10E3, 50E3, 100E3)
if(bin_size==20E3) bin_sizes = c(20E3, 40E3, 100E3)
if(bin_size==25E3) bin_sizes = c(25E3, 50E3, 100E3)
if(bin_size==40E3) bin_sizes = c(40E3, 80E3)
if(bin_size==50E3) bin_sizes = c(50E3, 100E3)
Note that this strategy is currently only available for hg19, hg38, mm9 and mm10 genome for which we generated high quality reference compartments using Hi-C data from: GSE63525 for hg19, https://data.4dnucleome.org/files-processed/4DNFI1UEG1HD for hg38, GSM3959427 for mm9, http://hicfiles.s3.amazonaws.com/external/bonev/CN_mapq30.hic for mm10.
(2) Support for other genomes
Although CALDER was mainly tested on human and mouse dataset, it can be applied to dataset from other genomes. One additional information is required in such case: a feature_track presumably positively correlated with compartment score (thus higher values in A than in B compartment). This information will be used for correctly determing the A/B direction. Some suggested tracks are gene density, H3K27ac, H3K4me1, H3K4me2, H3K4me3, H3K36me3 (or negative transform of H3K9me3) signals. Note that this information will not alter the hierarchical compartment/TAD structure, and can come from any external study with matched genome. An example of feature_track is given in the Usage section.
Installation
Make sure all dependencies have been installed:
- R.utils (>= 2.9.0),
- doParallel (>= 1.0.15),
- ape (>= 5.3),
- dendextend (>= 1.12.0),
- fitdistrplus (>= 1.0.14),
- igraph (>= 1.2.4.1),
- Matrix (>= 1.2.17),
- rARPACK (>= 0.11.0),
- factoextra (>= 1.0.5),
- maptools (>= 0.9.5),
- data.table (>= 1.12.2),
- fields (>= 9.8.3),
- GenomicRanges (>= 1.36.0)
- ggplot2 (>= 3.3.5)
- strawr (>= 0.0.9)
Clone its repository and install it from source:
git clone https://github.com/CSOgroup/CALDER.git
install.packages(path_to_CALDER, repos = NULL, type="source") ## install from the cloned source file
Please contact yliueagle@googlemail.com for any questions about installation.
install CALDER and dependencies automaticly:
if (!requireNamespace("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE))
install.packages("BiocManager")
BiocManager::install("GenomicRanges")
install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("CSOgroup/CALDER")
Usage
CALDER contains three modules: (1) compute chromatin domains; (2) derive their hierarchical organization and obtain sub-compartments; (3) compute nested sub-domains within each compartment domain.
Input data format
CALDER works on contact matrices compatable with that generated by Juicer tools (https://github.com/aidenlab/juicer), either a .hic file, or three-column dump table retrieved by the juicer dump (or straw) command (https://github.com/aidenlab/juicer/wiki/Data-Extraction):
16050000 16050000 10106.306
16050000 16060000 2259.247
16060000 16060000 7748.551
16050000 16070000 1251.3663
16060000 16070000 4456.1245
16070000 16070000 4211.7393
16050000 16080000 522.0705
16060000 16080000 983.1761
16070000 16080000 1996.749
...
feature_track should be a data.frame or data.table of 4 columns (chr, start, end, score), and can be generated directly from conventional format such as bed or wig, see the example:
library(rtracklayer)
feature_track = import('ENCFF934YOE.bigWig') ## from ENCODE https://www.encodeproject.org/files/ENCFF934YOE/@@download/ENCFF934YOE.bigWig
feature_track = data.table::as.data.table(feature_track)[, c(1:3, 6)]
> feature_track
chr start end score
chr1 534179 534353 2.80512
chr1 534354 572399 0
chr1 572400 572574 2.80512
chr1 572575 628400 0
... ... ... ...
chrY 59031457 59032403 0
chrY 59032404 59032413 0.92023
chrY 59032414 59032415 0.96625
chrY 59032416 59032456 0.92023
chrY 59032457 59032578 0.78875
Example usage (1): use contact matrix file in dump format as input
chrs = c(21:22)
## demo contact matrices in dump format
contact_file_dump = as.list(system.file("extdata", sprintf("mat_chr%s_10kb_ob.txt.gz", chrs),
package='CALDER'))
names(contact_file_dump) = chrs
## Run CALDER to compute compartments but not nested sub-domains
CALDER(contact_file_dump=contact_file_dump,
chrs=chrs,
bin_size=10E3,
genome='hg19',
save_dir=save_dir,
save_intermediate_data=FALSE,
n_cores=2,
sub_domains=FALSE)
## Run CALDER to compute compartments and nested sub-domains / will take more time
CALDER(contact_file_dump=contact_file_dump,
chrs=chrs,
bin_size=10E3,
genome='hg19',
save_dir=save_dir,
save_intermediate_data=TRUE,
n_cores=2,
sub_domains=TRUE)
Example (2): use contact matrices stored in an R list
chrs = c(21:22)
contact_file_dump = as.list(system.file("extdata", sprintf("mat_chr%s_10kb_ob.txt.gz", chrs),
package='CALDER'))
names(contact_file_dump) = chrs
contact_tab_dump = lapply(contact_file_dump, data.table::fread)
CALDER(contact_tab_dump=contact_tab_dump,
chrs=chrs,
bin_size=10E3,
genome='hg19',
save_dir=save_dir,
save_intermediate_data=FALSE,
n_cores=2,
sub_domains=FALSE)
Example (3): use .hic file as input
chrs = c(21:22)
hic_file = 'HMEC_combined_30.hic' ## can be downloaded from https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/series/GSE63nnn/GSE63525/suppl/GSE63525_HMEC_combined_30.hic
CALDER(contact_file_hic=hic_file,
chrs=chrs,
bin_size=10E3,
genome='hg19',
save_dir=save_dir,
save_intermediate_data=FALSE,
n_cores=2,
sub_domains=FALSE)
Example (4): run CALDER on other genomes
## prepare feature_track
library(rtracklayer)
feature_track_raw = import('ENCFF934YOE.bigWig') ## from ENCODE https://www.encodeproject.org/files/ENCFF934YOE/@@download/ENCFF934YOE.bigWig
feature_track = data.table::as.data.table(feature_track_raw)[, c(1:3, 6)]
## Run CALDER
chrs = c(21:22)
contact_file_dump = as.list(system.file("extdata", sprintf("mat_chr%s_10kb_ob.txt.gz", chrs),
package='CALDER'))
names(contact_file_dump) = chrs
CALDER(contact_file_dump=contact_file_dump,
chrs=chrs,
bin_size=10E3,
genome=others,
save_dir=save_dir,
feature_track=feature_track,
save_intermediate_data=FALSE,
n_cores=2,
sub_domains=FALSE)
Paramters:
| Name | Description |
| --------------------- | ----------------------- |
| chrs | A vector of chromosome names to be analyzed, with or without 'chr'
| contact_file_dump |A list of contact files in dump format, named by chrs. Each contact file stores the contact information of the corresponding chr. Only one of contact_file_dump, contact_tab_dump, contact_file_hic should be provided
| contact_tab_dump | A list of contact table in dump format, named by chrs, stored as an R object. Only one of contact_file_dump, contact_tab_dump, contact_file_hic should be provided
| contact_file_hic | A hic file generated by Juicer tools. It should contain all chromosomes in chrs. Only one of contact_file_dump, contact_tab_dump, contact_file_hic should be provided
| genome | One of 'hg19', 'hg38', 'mm9', 'mm10', 'others' (default). These compartments will be used as reference compartments for optimized bin_size selection. If genome = others, a feature_track should be provided (see below) and no optimized bin_size selection will be performed
| save_dir | the directory to be created for saving outputs
| bin_size | The bin_size (resolution) to run CALDER. bin_size should be consistent with the data resolution in contact_file_dump or contact_tab_dump if these files are provided as input, otherwise bin_size should exist in contact_file_hic. Recommended bin_size is between 10000 to 100000
| single_binsize_only | logical. If TRUE, CALDER will compute compartments only using the bin_size specified by the user and not do bin size optimization
| feature_track | A genomic feature track in data.frame or data.table format. This track will be used for determing the A/B compartment direction when genome=others and should presumably have higher values in A than in B compartment. Some suggested tracks can be gene density, H3K27ac, H3K4me1, H3K4me2, H3K4me3, H3K36me3 (or negative transform of H3K9me3 signals)
| save_intermediate_data | logical. If TRUE, an intermediate_data will be saved. This file can be used for computing nested sub-domains later on
| n_cores | integer. Number of cores to be registered for running CALDER in parallel
| sub_domains | logical, whether to compute nested sub-domains
Output:
chrxx_domain_hierachy.tsv
- information of compartment domain and their hierarchical organization. The hierarchical structure is fully represented by
compartment_label, for example,B.2.2.2andB.2.2.1are two sub-branches ofB.2.2. Thepos_endcolumn specifies all compartment domain borders, except when it is marked asgap, which indicates it is the border of a gap chromsome region that has too few contacts and was excluded from the analysis (e.g., due to low mappability, deletion, technique flaw)
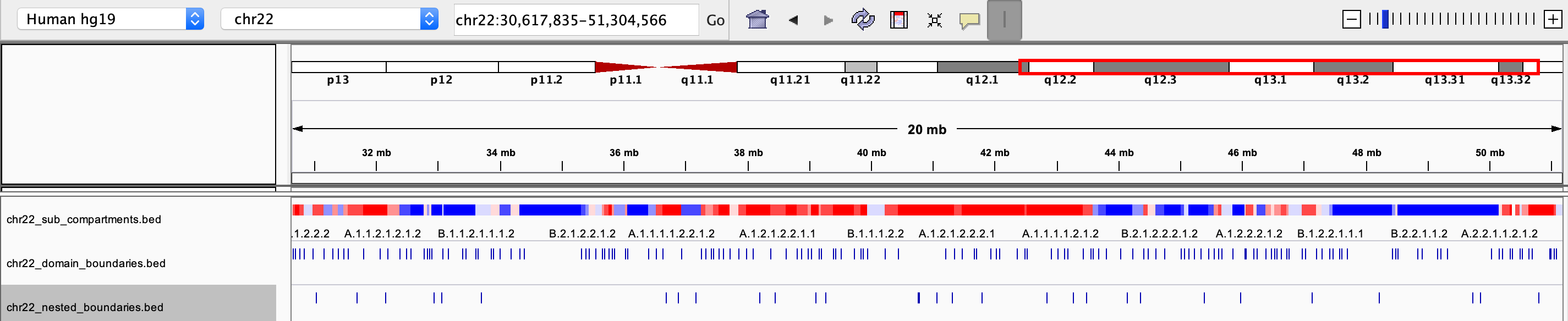
chrxx_sub_compartments.bed
- a .bed file containing the sub-compartment information, that can be visualized in IGV. Different colors were used to distinguish compartments (at the resolution of 8 sub-compartments)
chrxx_domain_boundaries.bed
- a .bed file containing the chromatin domains boundaries, that can be visualized in IGV
chrxx_nested_boundaries.bed
- a .bed file containing the nested sub-domain boundaries, that can be visualized in IGV
chrxx_intermediate_data.Rds
- an Rds file storing the intermediate_data that can be used to compute nested sub-domains (if CALDER is run in two seperated steps)
chrxx_log.txt, chrxx_sub_domains_log.txt
- log file storing the status and running time of each step
Output Structure
The output of the workflow is stored in the folder specified by --save_dir ("results" by default) and will look like this:
save_dir/
|-- intermediate_data
| |-- sub_compartments
| | |-- 100kb
| | | |-- chr21_domain_boundaries.bed
| | | |-- chr21_domain_hierachy.tsv
| | | |-- chr21_log.txt
| | | |-- chr21_sub_compartments.bed
| | | |-- chr22_domain_boundaries.bed
| | | |-- chr22_domain_hierachy.tsv
| | | |-- chr22_log.txt
| | | `-- chr22_sub_compartments.bed
| | |-- 10kb
| | | |-- chr21_domain_boundaries.bed
| | | |-- chr21_domain_hierachy.tsv
| | | |-- chr21_intermediate_data.Rds
| | | |-- chr21_log.txt
| | | |-- chr21_sub_compartments.bed
| | | |-- chr22_domain_boundaries.bed
| | | |-- chr22_domain_hierachy.tsv
| | | |-- chr22_intermediate_data.Rds
| | | |-- chr22_log.txt
| | | `-- chr22_sub_compartments.bed
| | `-- 50kb
| | |-- chr21_domain_boundaries.bed
| | |-- chr21_domain_hierachy.tsv
| | |-- chr21_log.txt
| | |-- chr21_sub_compartments.bed
| | |-- chr22_domain_boundaries.bed
| | |-- chr22_domain_hierachy.tsv
| | |-- chr22_log.txt
| | `-- chr22_sub_compartments.bed
| `-- sub_domains
| |-- chr21_nested_boundaries.bed
| |-- chr21_sub_domains_log.txt
| |-- chr22_nested_boundaries.bed
| `-- chr22_sub_domains_log.txt
|-- sub_compartments ## final sub-compartments
| |-- all_sub_compartments.bed
| |-- all_sub_compartments.tsv
| |-- cor_with_ref.ALL.txt
| |-- cor_with_ref.pdf
| `-- cor_with_ref.txt
`-- sub_domains ## all nested boundaries
`-- all_nested_boundaries.bed
The saved .bed files can be view directly through IGV:
Runnig time:
For the computational requirement, running CALDER on the GM12878 Hi-C dataset at bin size of 40kb took 36 minutes to derive the chromatin domains and their hierarchy for all chromosomes (i.e., CALDER Step1 and Step2); 13 minutes to derive the nested sub-domains (i.e., CALDER Step3). At the bin size of 10kb, it took 1 h 44 minutes and 55 minutes correspondingly (server information: 40 cores, 64GB Ram, Intel(R) Xeon(R) Silver 4210 CPU @ 2.20GHz). The evaluation was done using a single core although CALDER can be run in a parallel manner.
Citation
If you use CALDER in your work, please cite: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-22666-3
Contact information
- Author: Yuanlong LIU
- Affiliation: Computational Systems Oncology group, Department of Computational Biology, University of Lausanne, Switzerland
- Email: yliueagle@googlemail.com